Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
PF: Gravity: Tiled Inversion Linear#
Invert data in tiles.
import os
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from SimPEG.potential_fields import gravity
from SimPEG import (
maps,
data,
data_misfit,
regularization,
optimization,
inverse_problem,
directives,
inversion,
)
from discretize.utils import mesh_builder_xyz, refine_tree_xyz, active_from_xyz
from SimPEG import utils
Setup#
Define the survey and model parameters
Create a global survey and mesh and simulate some data
# Create an array of observation points
xr = np.linspace(-30.0, 30.0, 20)
yr = np.linspace(-30.0, 30.0, 20)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(xr, yr)
# Move the observation points 5m above the topo
Z = -np.exp((X**2 + Y**2) / 75**2)
# Create a topo array
topo = np.c_[utils.mkvc(X.T), utils.mkvc(Y.T), utils.mkvc(Z.T)]
# Create station locations draped 0.1 m above topo
rxLoc = np.c_[utils.mkvc(X.T), utils.mkvc(Y.T), utils.mkvc(Z.T) + 0.1]
Divided and Conquer#
Split the data set in two and create sub-problems
# Mesh parameters
h = [5, 5, 5]
padDist = np.ones((3, 2)) * 100
octree_levels = [8, 4]
# Create tiles
local_indices = [rxLoc[:, 0] <= 0, rxLoc[:, 0] > 0]
local_surveys = []
local_meshes = []
for local_index in local_indices:
receivers = gravity.receivers.Point(rxLoc[local_index, :])
srcField = gravity.sources.SourceField([receivers])
local_survey = gravity.survey.Survey(srcField)
# Create a local mesh that covers all points, but refined on the local survey
local_mesh = mesh_builder_xyz(
topo, h, padding_distance=padDist, depth_core=100, mesh_type="tree"
)
local_mesh = refine_tree_xyz(
local_mesh,
local_survey.receiver_locations,
method="surface",
octree_levels=octree_levels,
finalize=True,
)
local_surveys.append(local_survey)
local_meshes.append(local_mesh)
/home/vsts/work/1/s/examples/02-gravity/plot_inv_grav_tiled.py:78: DeprecationWarning:
The surface option is deprecated as of `0.9.0` please update your code to use the `TreeMesh.refine_surface` functionality. It will be removed in a future version of discretize.
Global Mesh#
Create a global mesh survey for simulation
mesh = mesh_builder_xyz(
topo, h, padding_distance=padDist, depth_core=100, mesh_type="tree"
)
# This guarantees that the local meshes are always coarser or equal
for local_mesh in local_meshes:
mesh.insert_cells(
local_mesh.gridCC,
local_mesh.cell_levels_by_index(np.arange(local_mesh.nC)),
finalize=False,
)
mesh.finalize()
# Define an active cells from topo
activeCells = active_from_xyz(mesh, topo)
nC = int(activeCells.sum())
# We can now create a density model and generate data
# Here a simple block in half-space
# Get the indices of the magnetized block
model = np.zeros(mesh.nC)
ind = utils.model_builder.getIndicesBlock(
np.r_[-10, -10, -30],
np.r_[10, 10, -10],
mesh.gridCC,
)[0]
# Assign magnetization values
model[ind] = 0.3
# Remove air cells
model = model[activeCells]
# Create reduced identity map
idenMap = maps.IdentityMap(nP=nC)
# Create a global survey just for simulation of data
receivers = gravity.receivers.Point(rxLoc)
srcField = gravity.sources.SourceField([receivers])
survey = gravity.survey.Survey(srcField)
# Create the forward simulation for the global dataset
simulation = gravity.simulation.Simulation3DIntegral(
survey=survey, mesh=mesh, rhoMap=idenMap, ind_active=activeCells
)
# Compute linear forward operator and compute some data
d = simulation.fields(model)
# Add noise and uncertainties
# We add some random Gaussian noise (1nT)
synthetic_data = d + np.random.randn(len(d)) * 1e-3
wd = np.ones(len(synthetic_data)) * 1e-3 # Assign flat uncertainties
Tiled misfits
local_misfits = []
for ii, local_survey in enumerate(local_surveys):
tile_map = maps.TileMap(mesh, activeCells, local_meshes[ii])
local_actives = tile_map.local_active
# Create the forward simulation
simulation = gravity.simulation.Simulation3DIntegral(
survey=local_survey,
mesh=local_meshes[ii],
rhoMap=tile_map,
ind_active=local_actives,
sensitivity_path=os.path.join("Inversion", f"Tile{ii}.zarr"),
)
data_object = data.Data(
local_survey,
dobs=synthetic_data[local_indices[ii]],
standard_deviation=wd[local_indices[ii]],
)
local_misfits.append(
data_misfit.L2DataMisfit(data=data_object, simulation=simulation)
)
# Our global misfit
global_misfit = local_misfits[0] + local_misfits[1]
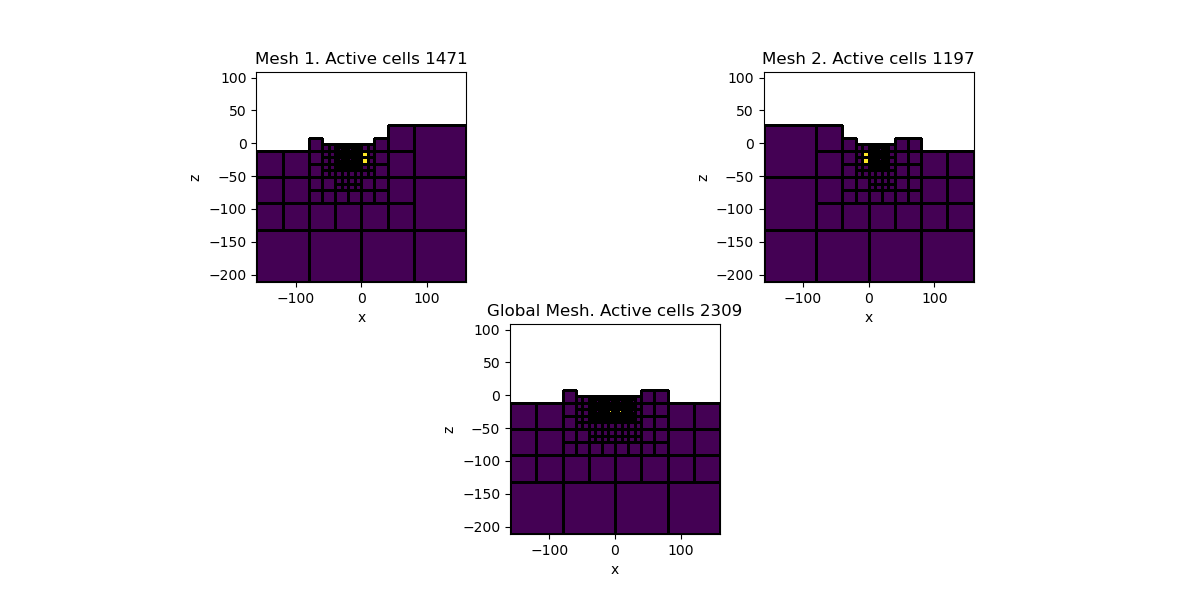
# Plot the model on different meshes
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
for ii, local_misfit in enumerate(local_misfits):
local_mesh = local_misfit.simulation.mesh
local_map = local_misfit.simulation.rhoMap
inject_local = maps.InjectActiveCells(local_mesh, local_map.local_active, np.nan)
ax = plt.subplot(2, 2, ii + 1)
local_mesh.plot_slice(
inject_local * (local_map * model), normal="Y", ax=ax, grid=True
)
ax.set_aspect("equal")
ax.set_title(f"Mesh {ii+1}. Active cells {local_map.local_active.sum()}")
# Create active map to go from reduce set to full
inject_global = maps.InjectActiveCells(mesh, activeCells, np.nan)
ax = plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
mesh.plot_slice(inject_global * model, normal="Y", ax=ax, grid=True)
ax.set_title(f"Global Mesh. Active cells {activeCells.sum()}")
ax.set_aspect("equal")
plt.show()
Invert on the global mesh
# Create reduced identity map
idenMap = maps.IdentityMap(nP=nC)
# Create a regularization
reg = regularization.Sparse(mesh, active_cells=activeCells, mapping=idenMap)
m0 = np.ones(nC) * 1e-4 # Starting model
# Add directives to the inversion
opt = optimization.ProjectedGNCG(
maxIter=100, lower=-1.0, upper=1.0, maxIterLS=20, maxIterCG=10, tolCG=1e-3
)
invProb = inverse_problem.BaseInvProblem(global_misfit, reg, opt)
betaest = directives.BetaEstimate_ByEig(beta0_ratio=1e-1)
# Here is where the norms are applied
# Use a threshold parameter empirically based on the distribution of
# model parameters
update_IRLS = directives.Update_IRLS(
f_min_change=1e-4,
max_irls_iterations=0,
coolEpsFact=1.5,
beta_tol=1e-2,
)
saveDict = directives.SaveOutputEveryIteration(save_txt=False)
update_Jacobi = directives.UpdatePreconditioner()
sensitivity_weights = directives.UpdateSensitivityWeights(everyIter=False)
inv = inversion.BaseInversion(
invProb,
directiveList=[update_IRLS, sensitivity_weights, betaest, update_Jacobi, saveDict],
)
# Run the inversion
mrec = inv.run(m0)
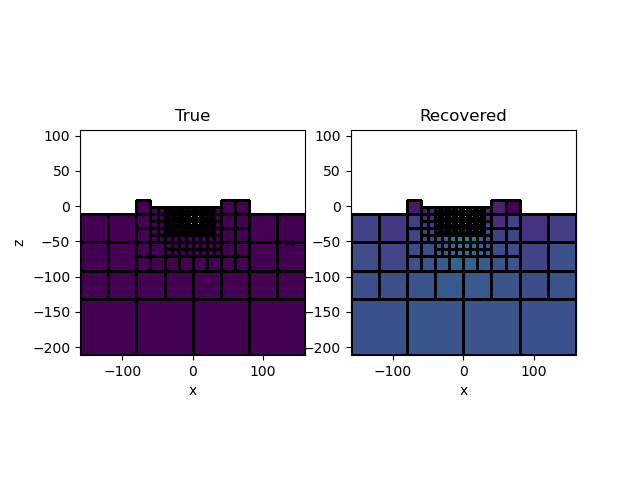
# Plot the result
ax = plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
mesh.plot_slice(inject_global * model, normal="Y", ax=ax, grid=True)
ax.set_title("True")
ax.set_aspect("equal")
ax = plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
mesh.plot_slice(inject_global * mrec, normal="Y", ax=ax, grid=True)
ax.set_title("Recovered")
ax.set_aspect("equal")
plt.show()
/home/vsts/work/1/s/examples/02-gravity/plot_inv_grav_tiled.py:246: UserWarning:
'everyIter' property is deprecated and will be removed in SimPEG 0.20.0.Please use 'every_iteration'.
SimPEG.InvProblem will set Regularization.reference_model to m0.
SimPEG.InvProblem will set Regularization.reference_model to m0.
SimPEG.InvProblem will set Regularization.reference_model to m0.
SimPEG.InvProblem will set Regularization.reference_model to m0.
SimPEG.InvProblem is setting bfgsH0 to the inverse of the eval2Deriv.
***Done using the default solver Pardiso and no solver_opts.***
model has any nan: 0
=============================== Projected GNCG ===============================
# beta phi_d phi_m f |proj(x-g)-x| LS Comment
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
x0 has any nan: 0
0 2.14e+03 4.26e+04 0.00e+00 4.26e+04 4.80e+01 0
1 1.07e+03 5.20e+03 1.78e+00 7.10e+03 4.77e+01 0
2 5.35e+02 2.91e+03 3.29e+00 4.67e+03 4.75e+01 0 Skip BFGS
3 2.67e+02 1.41e+03 5.25e+00 2.81e+03 4.73e+01 0 Skip BFGS
4 1.34e+02 6.54e+02 7.20e+00 1.62e+03 4.69e+01 0 Skip BFGS
5 6.69e+01 3.32e+02 8.84e+00 9.23e+02 4.63e+01 0 Skip BFGS
6 3.34e+01 2.09e+02 1.01e+01 5.47e+02 4.51e+01 0 Skip BFGS
Reached starting chifact with l2-norm regularization: Start IRLS steps...
irls_threshold 0.07444388852989561
Reach maximum number of IRLS cycles: 0
------------------------- STOP! -------------------------
1 : |fc-fOld| = 0.0000e+00 <= tolF*(1+|f0|) = 4.2557e+03
1 : |xc-x_last| = 3.0825e-02 <= tolX*(1+|x0|) = 1.0048e-01
0 : |proj(x-g)-x| = 4.5138e+01 <= tolG = 1.0000e-01
0 : |proj(x-g)-x| = 4.5138e+01 <= 1e3*eps = 1.0000e-02
0 : maxIter = 100 <= iter = 7
------------------------- DONE! -------------------------
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 4.371 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 15 MB