simpeg.maps.ParametricSplineMap#
- class simpeg.maps.ParametricSplineMap(mesh, pts, ptsv=None, order=3, logSigma=True, normal='x', slope=10000.0)[source]#
Bases:
IdentityMapMapping to parameterize the boundary between two geological units using spline interpolation.
\[g = f(x)-y\]Define the model as:
\[m = [\sigma_1, \sigma_2, y]\]- Parameters:
- mesh
discretize.BaseMesh A discretize mesh
- pts(
n)numpy.ndarray Points for the 1D spline tie points.
- ptsv(2) array_like
Points for linear interpolation between two splines in 3D.
- order
int Order of the spline mapping; e.g. 3 is cubic spline
- logSigmabool
If
True, \(\sigma_1\) and \(\sigma_2\) represent the natural log of some physical property value for each unit.- normal{‘x’, ‘y’, ‘z’}
Defines the general direction of the normal vector for the interface.
- slope
float Parameter for defining the sharpness of the boundary. The sharpness is increased if slope is large.
- mesh
Attributes
Determine whether or not this mapping is a linear operation.
Whether the input needs to be transformed by an exponential
The mesh used for the mapping
Number of parameters the mapping acts on
The projection axis.
The number of points.
Order of the spline mapping.
Points for the spline.
Bottom and top values for the 3D spline surface.
Dimensions of the mapping operator
Sharpness of the boundary.
Methods
deriv(m[, v])Derivative of the mapping with respect to the input parameters.
dot(map1)Multiply two mappings to create a
simpeg.maps.ComboMap.inverse(D)The transform inverse is not implemented.
test([m, num, random_seed])Derivative test for the mapping.
Examples
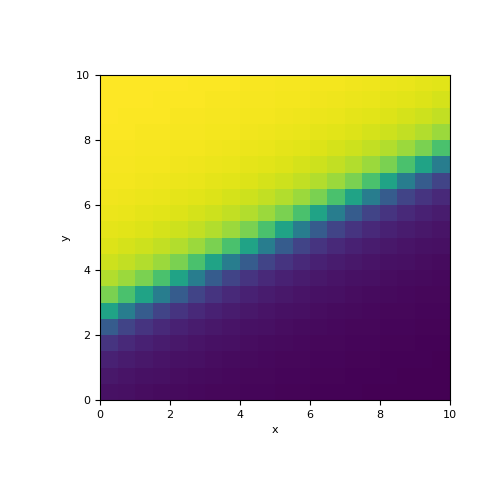
In this example, we define a 2 layered model with a sloping interface on a 2D mesh. The model consists of the physical property values for the layers and the known elevations for the interface at the horizontal positions supplied when creating the mapping.
>>> from simpeg.maps import ParametricSplineMap >>> from discretize import TensorMesh >>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> h = 0.5*np.ones(20) >>> mesh = TensorMesh([h, h])
>>> x = np.linspace(0, 10, 6) >>> y = 0.5*x + 2.5
>>> model = np.r_[10., 0., y] >>> mapping = ParametricSplineMap(mesh, x, order=2, normal='Y', slope=2)
>>> fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5)) >>> ax = fig.add_subplot(111) >>> mesh.plot_image(mapping * model, ax=ax)
(
Source code,png,pdf)