SimPEG.maps.ExpMap#
- class SimPEG.maps.ExpMap(mesh=None, nP=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
IdentityMapMapping that computes the natural exponentials of the model parameters.
Where \(\mathbf{m}\) is a set of model parameters,
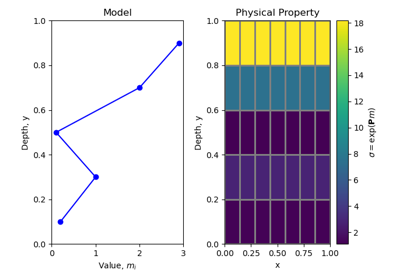
ExpMapcreates a mapping \(\mathbf{u}(\mathbf{m})\) that computes the natural exponential of every element in \(\mathbf{m}\); i.e.:\[\mathbf{u}(\mathbf{m}) = exp(\mathbf{m})\]ExpMapis commonly used when working with physical properties whose values span many orders of magnitude (e.g. the electrical conductivity \(\sigma\)). By usingExpMap, we can invert for a model that represents the natural log of a set of physical property values, i.e. when \(m = log(\sigma)\)- Parameters:
- mesh
discretize.BaseMesh The number of parameters accepted by the mapping is set to equal the number of mesh cells.
- nP
int Set the number of parameters accepted by the mapping directly. Used if the number of parameters is known. Used generally when the number of parameters is not equal to the number of cells in a mesh.
- mesh
Attributes
Determine whether or not this mapping is a linear operation.
The mesh used for the mapping
Number of parameters the mapping acts on.
Dimensions of the mapping operator
Methods
deriv(m[, v])Derivative of mapping with respect to the input parameters.
dot(map1)Multiply two mappings to create a
SimPEG.maps.ComboMap.inverse(D)Apply the inverse of the exponential mapping to an array.
test([m, num])Derivative test for the mapping.
Galleries and Tutorials using SimPEG.maps.ExpMap#
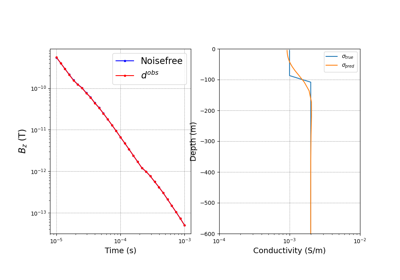
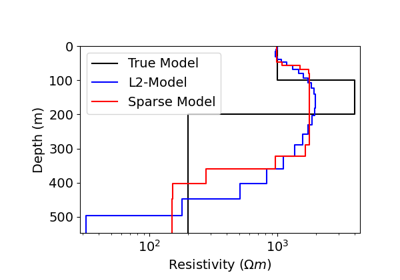
Heagy et al., 2017 1D RESOLVE and SkyTEM Bookpurnong Inversions
Heagy et al., 2017 1D RESOLVE Bookpurnong Inversion
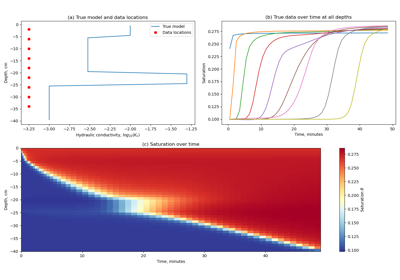
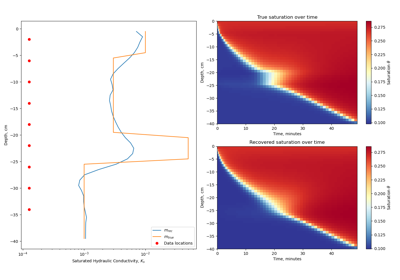
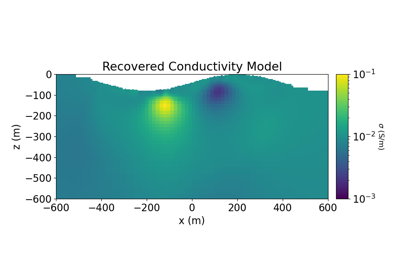
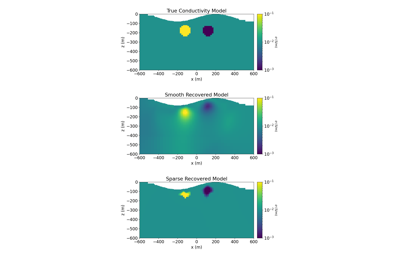
2.5D DC Resistivity and IP Least-Squares Inversion
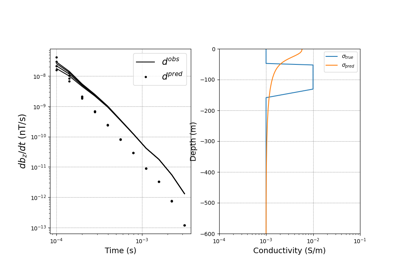
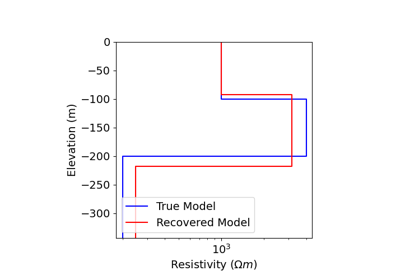
1D Inversion of Time-Domain Data for a Single Sounding