simpeg.optimization.InexactGaussNewton#
- class simpeg.optimization.InexactGaussNewton(*, cg_rtol=0.1, cg_atol=0.0, cg_maxiter=5, **kwargs)[source]#
-
Minimizes using CG as the inexact solver of
\[\mathbf{H p = -g}\]By default BFGS is used as the preconditioner.
Use nbfgs to set the memory limitation of BFGS.
To set the initial H0 to be used in BFGS, set bfgsH0 to be a simpeg.Solver
Attributes
The approximate Hessian inverse is used to precondition CG.
Approximate Hessian used in preconditioning the problem.
A used defined callback function.
Absolute tolerance for inner CG iterations.
Maximum number of CG iterations.
Relative tolerance for inner CG iterations.
InexactCG.maxIterCG has been deprecated.
InexactCG.tolCG has been deprecated.
counter
parent
print_type
Methods
bfgsrec(k, n, nn, S, Y, d)BFGS recursion
doEndIteration(xt)Operation called at the end of each minimize iteration.
Called at the start of each minimize iteration. If you have things that also need to run in the method doStartIteration, you can create a method::.
Return the direction to search along for a minimum value.
finish()Called at the end of the optimization. If you have things that also need to run in the method finish, you can create a method::.
minimize(evalFunction, x0)Minimizes the function (evalFunction) starting at the location x0.
Changes the search direction based on some sort of linesearch or trust-region criteria.
Called if modifySearchDirection fails to find a descent direction.
printDone([inLS])Called at the end of the optimization routine.
printInit([inLS])Called at the beginning of the optimization routine.
printIter([inLS])Called directly after function evaluations.
projection(p)Projects a model onto bounds (if given)
Scales the search direction if appropriate.
startup(x0)Called at the start of any new minimize call.
bfgs
recall
remember
save
stoppingCriteria
Galleries and Tutorials using simpeg.optimization.InexactGaussNewton#
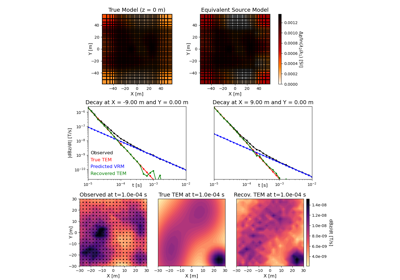
Method of Equivalent Sources for Removing VRM Responses
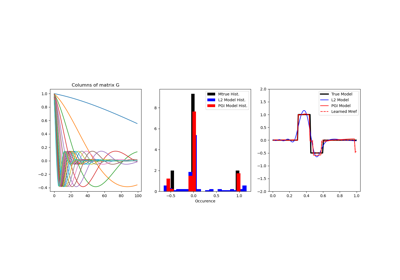
Petrophysically guided inversion (PGI): Linear example
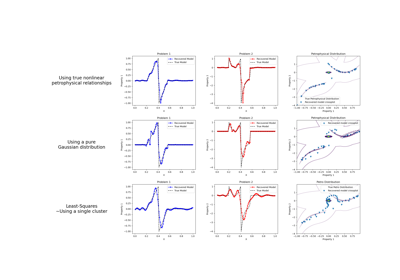
Petrophysically guided inversion: Joint linear example with nonlinear relationships
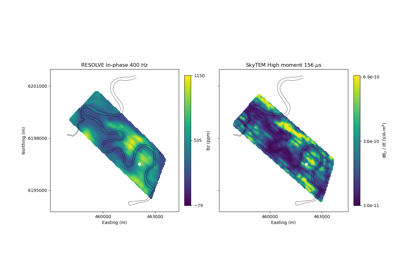
Heagy et al., 2017 1D RESOLVE and SkyTEM Bookpurnong Inversions
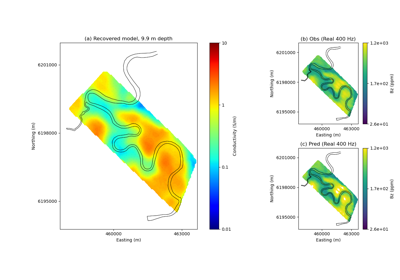
Heagy et al., 2017 1D RESOLVE Bookpurnong Inversion
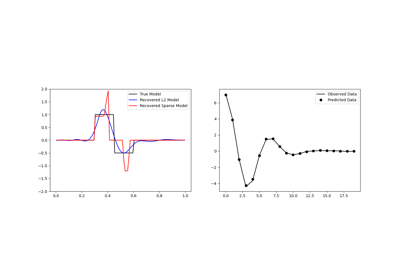
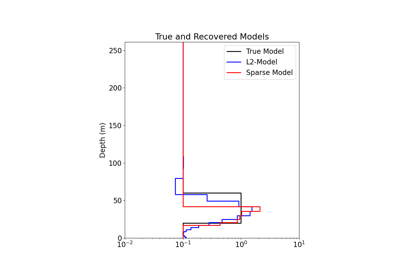
Sparse Inversion with Iteratively Re-Weighted Least-Squares
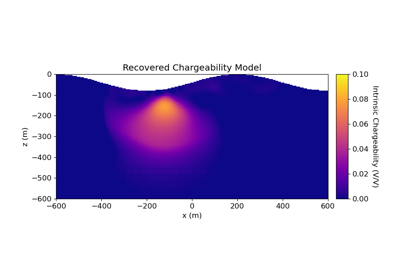
2.5D DC Resistivity and IP Least-Squares Inversion
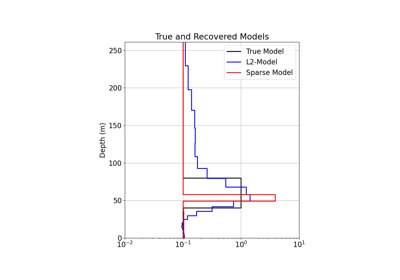
1D Inversion of Time-Domain Data for a Single Sounding
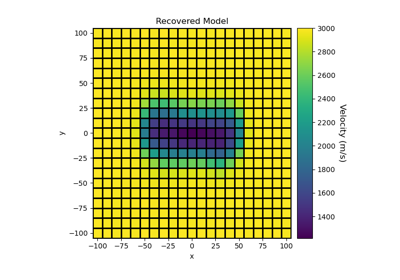
Sparse Norm Inversion of 2D Seismic Tomography Data
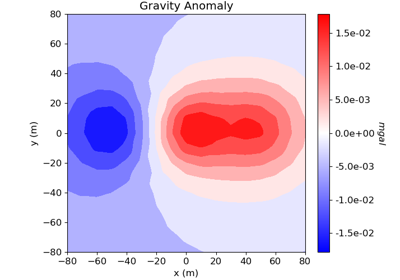
Cross-gradient Joint Inversion of Gravity and Magnetic Anomaly Data
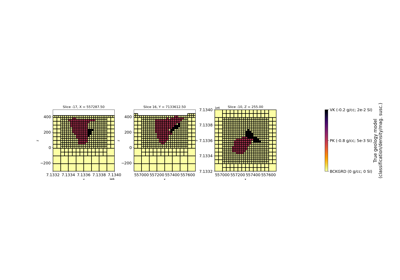
Joint PGI of Gravity + Magnetic on an Octree mesh using full petrophysical information
Joint PGI of Gravity + Magnetic on an Octree mesh without petrophysical information