Note
Click here to download the full example code
Predict Response from a Conductive and Magnetically Viscous Earth#
Here, we predict the vertical db/dt response over a conductive and magnetically viscous Earth for a small coincident loop system. Following the theory, the total response is approximately equal to the sum of the inductive and VRM responses modelled separately. The SimPEG.VRM module is used to model the VRM response while an analytic solution for a conductive half-space is used to model the inductive response.
Import modules#
from SimPEG.electromagnetics import viscous_remanent_magnetization as VRM
import numpy as np
import discretize
from SimPEG import mkvc, maps
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
Defining the mesh#
Defining the model#
Create xi model (amalgamated magnetic property). Here the model is made by summing a set of 3D Gaussian distributions. And only active cells have a model value.
topoCells = mesh.gridCC[:, 2] < 0.0 # Define topography
xyzc = mesh.gridCC[topoCells, :]
c = 2 * np.pi * 8 ** 2
pc = np.r_[4e-4, 4e-4, 4e-4, 6e-4, 8e-4, 6e-4, 8e-4, 8e-4]
x_0 = np.r_[50.0, -50.0, -40.0, -20.0, -15.0, 20.0, -10.0, 25.0]
y_0 = np.r_[0.0, 0.0, 40.0, 10.0, -20.0, 15.0, 0.0, 0.0]
z_0 = np.r_[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
var_x = c * np.r_[3.0, 3.0, 3.0, 1.0, 3.0, 0.5, 0.1, 0.1]
var_y = c * np.r_[20.0, 20.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.4, 0.5, 0.1, 0.4]
var_z = c * np.r_[1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0]
xi_true = np.zeros(np.shape(xyzc[:, 0]))
for ii in range(0, 8):
xi_true += (
pc[ii]
* np.exp(-((xyzc[:, 0] - x_0[ii]) ** 2) / var_x[ii])
* np.exp(-((xyzc[:, 1] - y_0[ii]) ** 2) / var_y[ii])
* np.exp(-((xyzc[:, 2] - z_0[ii]) ** 2) / var_z[ii])
)
xi_true += 1e-5
Survey#
Here we must set the transmitter waveform, which defines the off-time decay of the VRM response. Next we define the sources, receivers and time channels for the survey. Our example is similar to an EM-63 survey.
waveform = VRM.waveforms.StepOff()
times = np.logspace(-5, -2, 31) # Observation times
x, y = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-30, 30, 21), np.linspace(-30, 30, 21))
z = 0.5 * np.ones(x.shape)
loc = np.c_[mkvc(x), mkvc(y), mkvc(z)] # Src and Rx Locations
src_list_vrm = []
for pp in range(0, loc.shape[0]):
loc_pp = np.reshape(loc[pp, :], (1, 3))
rx_list_vrm = [
VRM.Rx.Point(loc_pp, times=times, field_type="dbdt", orientation="z")
]
src_list_vrm.append(
VRM.Src.MagDipole(rx_list_vrm, mkvc(loc[pp, :]), [0.0, 0.0, 0.01], waveform)
)
survey_vrm = VRM.Survey(src_list_vrm)
Simulation#
For the VRM problem, we used a sensitivity refinement strategy for cells that are proximal to transmitters. This is controlled through the refinement_factor and refinement_distance properties.
# Defining the problem
problem_vrm = VRM.Simulation3DLinear(
mesh,
survey=survey_vrm,
indActive=topoCells,
refinement_factor=3,
refinement_distance=[1.25, 2.5, 3.75],
)
# Predict VRM response
fields_vrm = problem_vrm.fields(xi_true)
n_times = len(times)
n_loc = loc.shape[0]
fields_vrm = np.reshape(fields_vrm, (n_loc, n_times))
# Add an artificial TEM response. An analytic solution for the response near
# the surface of a conductive half-space (Nabighian, 1979) is scaled at each
# location to provide lateral variability in the TEM response.
sig = 1e-1
mu0 = 4 * np.pi * 1e-7
fields_tem = -(sig ** 1.5) * mu0 ** 2.5 * times ** -2.5 / (20 * np.pi ** 1.5)
fields_tem = np.kron(np.ones((n_loc, 1)), np.reshape(fields_tem, (1, n_times)))
c = (
np.exp(-((loc[:, 0] - 10) ** 2) / (25 ** 2))
* np.exp(-((loc[:, 1] - 20) ** 2) / (35 ** 2))
+ np.exp(-((loc[:, 0] + 20) ** 2) / (20 ** 2))
* np.exp(-((loc[:, 1] + 20) ** 2) / (40 ** 2))
+ 1.5
* np.exp(-((loc[:, 0] - 25) ** 2) / (10 ** 2))
* np.exp(-((loc[:, 1] + 25) ** 2) / (10 ** 2))
+ 0.25
)
c = np.kron(np.reshape(c, (len(c), 1)), np.ones((1, n_times)))
fields_tem = c * fields_tem
CREATING T MATRIX
CREATING A MATRIX
Plotting#
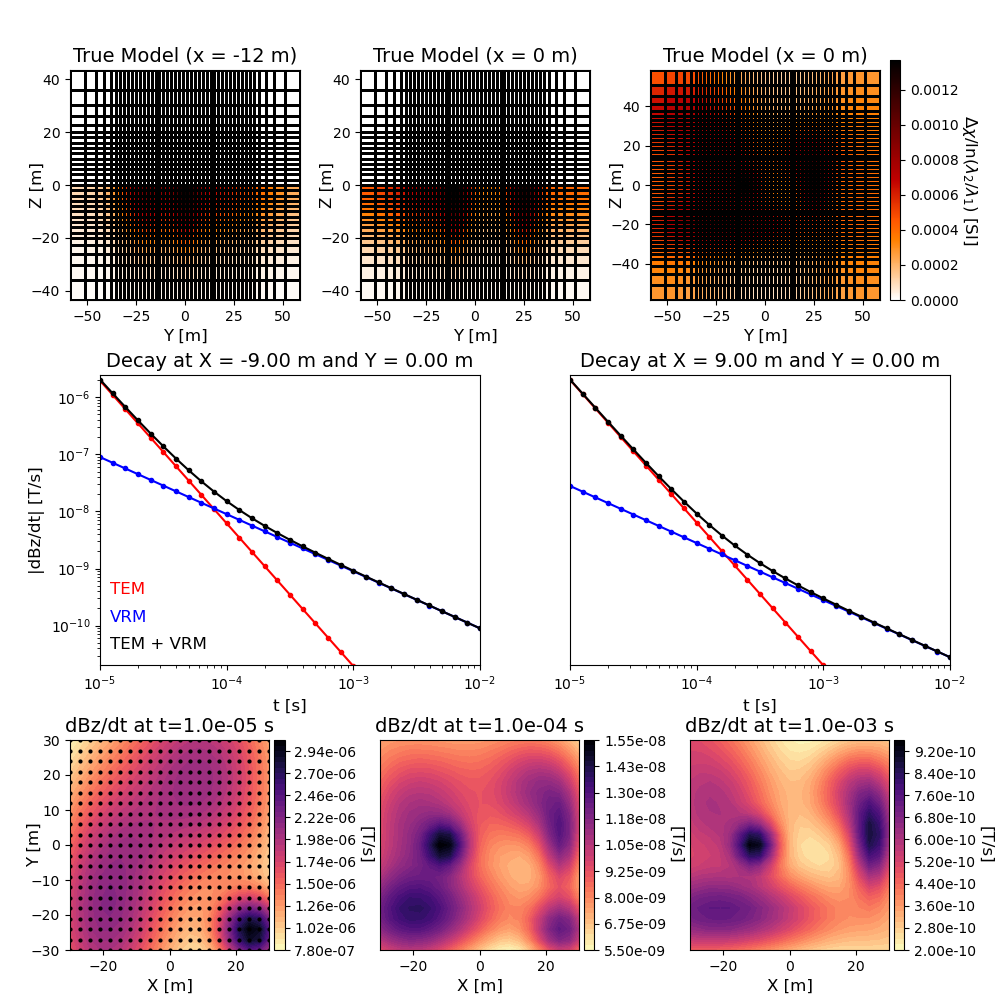
# Plotting the model
Fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
font_size = 12
plotMap = maps.InjectActiveCells(mesh, topoCells, 0.0) # Maps to mesh
ax1 = 4 * [None]
cplot1 = 3 * [None]
view_str = ["X", "Y", "Z"]
param_1 = [ncx, ncy, ncz]
param_2 = [6, 0, 1]
param_3 = [-12, 0, 0]
for qq in range(0, 3):
ax1[qq] = Fig.add_axes([0.07 + qq * 0.29, 0.7, 0.23, 0.23])
cplot1[qq] = mesh.plot_slice(
plotMap * xi_true,
normal=view_str[qq],
ind=int((param_1[qq] + 2 * npad) / 2 - param_2[qq]),
ax=ax1[qq],
grid=True,
pcolor_opts={"cmap": "gist_heat_r"},
)
cplot1[qq][0].set_clim((0.0, np.max(xi_true)))
ax1[qq].set_xlabel("Y [m]", fontsize=font_size)
ax1[qq].set_ylabel("Z [m]", fontsize=font_size, labelpad=-10)
ax1[qq].tick_params(labelsize=font_size - 2)
ax1[qq].set_title(
"True Model (x = {} m)".format(param_3[qq]), fontsize=font_size + 2
)
ax1[3] = Fig.add_axes([0.89, 0.7, 0.01, 0.24])
norm = mpl.colors.Normalize(vmin=0.0, vmax=np.max(xi_true))
cbar14 = mpl.colorbar.ColorbarBase(
ax1[3], cmap=mpl.cm.gist_heat_r, norm=norm, orientation="vertical"
)
cbar14.set_label(
"$\Delta \chi /$ln$(\lambda_2 / \lambda_1 )$ [SI]",
rotation=270,
labelpad=15,
size=font_size,
)
# Plotting the decay
ax2 = 2 * [None]
n = x.shape[0]
for qq in range(0, 2):
ax2[qq] = Fig.add_axes([0.1 + 0.47 * qq, 0.335, 0.38, 0.29])
k = int((n ** 2 - 1) / 2 - 3 * n * (-1) ** qq)
di_vrm = mkvc(np.abs(fields_vrm[k, :]))
di_tem = mkvc(np.abs(fields_tem[k, :]))
ax2[qq].loglog(times, di_tem, "r.-")
ax2[qq].loglog(times, di_vrm, "b.-")
ax2[qq].loglog(times, di_tem + di_vrm, "k.-")
ax2[qq].set_xlabel("t [s]", fontsize=font_size)
if qq == 0:
ax2[qq].set_ylabel("|dBz/dt| [T/s]", fontsize=font_size)
else:
ax2[qq].axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
ax2[qq].tick_params(labelsize=font_size - 2)
ax2[qq].set_xbound(np.min(times), np.max(times))
ax2[qq].set_ybound(1.2 * np.max(di_tem + di_vrm), 1e-5 * np.max(di_tem + di_vrm))
titlestr2 = (
"Decay at X = "
+ "{:.2f}".format(loc[k, 0])
+ " m and Y = "
+ "{:.2f}".format(loc[k, 1])
+ " m"
)
ax2[qq].set_title(titlestr2, fontsize=font_size + 2)
if qq == 0:
ax2[qq].text(
1.2e-5, 18 * np.max(di_tem) / 1e5, "TEM", fontsize=font_size, color="r"
)
ax2[qq].text(
1.2e-5, 6 * np.max(di_tem) / 1e5, "VRM", fontsize=font_size, color="b"
)
ax2[qq].text(
1.2e-5, 2 * np.max(di_tem) / 1e5, "TEM + VRM", fontsize=font_size, color="k"
)
# Plotting the TEM anomalies
ax3 = 3 * [None]
cplot3 = 3 * [None]
cbar3 = 3 * [None]
for qq in range(0, 3):
ax3[qq] = Fig.add_axes([0.07 + 0.31 * qq, 0.05, 0.24, 0.21])
d = np.reshape(np.abs(fields_tem[:, 10 * qq] + fields_vrm[:, 10 * qq]), (n, n))
cplot3[qq] = ax3[qq].contourf(x, y, d.T, 40, cmap="magma_r")
cbar3[qq] = plt.colorbar(cplot3[qq], ax=ax3[qq], pad=0.02, format="%.2e")
cbar3[qq].set_label("[T/s]", rotation=270, labelpad=12, size=font_size)
cbar3[qq].ax.tick_params(labelsize=font_size - 2)
ax3[qq].set_xlabel("X [m]", fontsize=font_size)
if qq == 0:
ax3[qq].scatter(x, y, color=(0, 0, 0), s=4)
ax3[qq].set_ylabel("Y [m]", fontsize=font_size, labelpad=-8)
else:
ax3[qq].axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
ax3[qq].tick_params(labelsize=font_size - 2)
ax3[qq].set_xbound(np.min(x), np.max(x))
ax3[qq].set_ybound(np.min(y), np.max(y))
titlestr3 = "dBz/dt at t=" + "{:.1e}".format(times[10 * qq]) + " s"
ax3[qq].set_title(titlestr3, fontsize=font_size + 2)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 14.970 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 120 MB