SimPEG.electromagnetics.time_domain.Simulation3DElectricField#
- class SimPEG.electromagnetics.time_domain.Simulation3DElectricField(mesh, survey=None, dt_threshold=1e-08, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
SimPEG.electromagnetics.time_domain.simulation.BaseTDEMSimulationSolve the EB-formulation of Maxwell’s equations for the electric field, e.
Starting with
\[\nabla \times \mathbf{e} + \frac{\partial \mathbf{b}}{\partial t} = \mathbf{s_m} \ \nabla \times \mu^{-1} \mathbf{b} - \sigma \mathbf{e} = \mathbf{s_e}\]we eliminate \(\frac{\partial b}{\partial t}\) using
\[\frac{\partial \mathbf{b}}{\partial t} = - \nabla \times \mathbf{e} + \mathbf{s_m}\]taking the time-derivative of Ampere’s law, we see
\[\frac{\partial}{\partial t}\left( \nabla \times \mu^{-1} \mathbf{b} - \sigma \mathbf{e} \right) = \frac{\partial \mathbf{s_e}}{\partial t} \ \nabla \times \mu^{-1} \frac{\partial \mathbf{b}}{\partial t} - \sigma \frac{\partial\mathbf{e}}{\partial t} = \frac{\partial \mathbf{s_e}}{\partial t}\]which gives us
\[\nabla \times \mu^{-1} \nabla \times \mathbf{e} + \sigma \frac{\partial\mathbf{e}}{\partial t} = \nabla \times \mu^{-1} \mathbf{s_m} + \frac{\partial \mathbf{s_e}}{\partial t}\]Methods
Fields_Derivsalias of
SimPEG.electromagnetics.time_domain.fields.FieldsDerivativesEBJtvec(m, v[, f])Jvec computes the adjoint of the sensitivity times a vector
fieldsPairalias of
SimPEG.electromagnetics.time_domain.fields.Fields3DElectricFieldgetAdiag(tInd)Diagonal of the system matrix at a given time index
getAdiagDeriv(tInd, u, v[, adjoint])Deriv of ADiag with respect to electrical conductivity
getAsubdiag(tInd)Matrix below the diagonal
getAsubdiagDeriv(tInd, u, v[, adjoint])Derivative of the matrix below the diagonal with respect to electrical conductivity
getRHS(tInd)right hand side
getAdc
getAdcDeriv
getRHSDeriv
Galleries and Tutorials using SimPEG.electromagnetics.time_domain.Simulation3DElectricField#
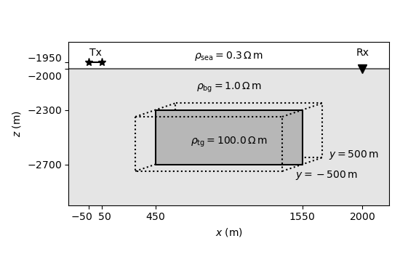
Time-domain CSEM for a resistive cube in a deep marine setting
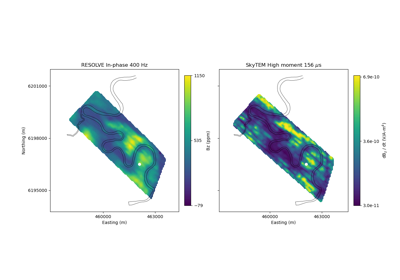
Heagy et al., 2017 1D RESOLVE and SkyTEM Bookpurnong Inversions